how to buy rimonabant nz without prescription

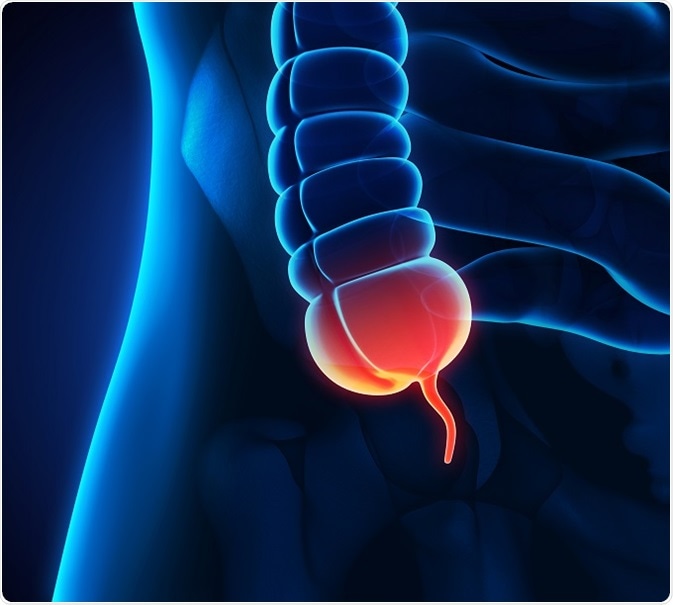
Cancers of the appendix are an extremely rare and deadly disease found in the abdominal region. The first section of the large intestine or colon is the appendix, which is a pouch-like tube attached to the cecum. The average length of the appendix is 10 centimeters (about 4 inches). It is considered to be a part of the alimentary canal.
Credit: Nerthuz/Shutterstock.com
In humans, the function of the appendix is unknown, even though it is believed to conceivably play a part in the immune system. Generally, it is considered tobe a part of the lymphatic, exocrine, buy generic retin coupon no prescription or endocrine system.
Appendix cancer occurs very rarely. Cancer of the appendix might have resulted to motivate appendicitis or breach of appendicitis. In most of the cases, this can be described as a first symptom of appendix cancer.
Depending on the types of cells within the tumor, appendix cancers are classified into different types, among which pseudomyxoma peritonei (PMP) is one.
Pseudomyxoma peritonei (PMP)
The term pseudomyxoma peritonei was first discovered in 1842 by Rokitansky. Due to the aperture of ovarian pseudomucinous cystomas, PMP was first used by Werthin 1884 to illustrate enormous intraperitoneal accumulation of gelatinous pseudomucin.
PMP is a relatively rare type of cancer that is simply converted to define “false mucinous tumor of the peritoneum.” In most of the cases, it originates in the appendix in the ovary. In rarer incidences, it can arise from other parts of the body, such as the bowel or the bladder.
In the case of PMP that arises in the appendix, the tumor generally begins developing from the inner lining of the organ as a small, slow growth, which can be termed as a polyp. The primary stage of this tumor does not produce any symptoms and it is barely discovered. When it gets larger, it develops through the wall of the appendix into the abdominal cavity where more tumors are formed.
Then, the mucinous tumor cells are allowed to get attached to the peritoneum, and they may also get linked to some of the abdominal organs such as the spleen, diaphragm, liver, ovaries, and uterus.
These cancerous cells produce mucus, which is collected in the abdomen as a jelly-like fluid called mucin. As it accumulates in huge quantities, it leads to symptom generation. This excess mucin is then allowed to run through the abdominal space where it, unfortunately, encircles the digestive organs, such as the colon, small bowel, and liver, leading to their malfunctioning.
Compared to other types of digestive cancers, PMP is a very slow growing disease.
Classification of PMP
There is no subtype identified for this kind of tumor. However, a few classes do exist based on the characteristic of the disease.
Based on severity
- Disseminated peritoneal adenomucinosis (DPAM) is one of the affable types of PMP which is not so harmful. Yet, it may present as the most advanced stage or can be life-threatening.
- Another type described by the doctors is PMCA, which can be expanded as peritoneal mucinous carcinomatosis. Here the cancer is exhibited by the cells from the tumor.
Based on the grade of the disease
PMP can be classified into three common categories based on the grade of the disease.
- LOW GRADE: Improper treatment leading to the deadly disease comes under the group of low-grade malignancy.
- HIGH GRADE: Treatment for the disease is very difficultbecause it contains “signet ring cells,” which are more destructive cancer cells.
- HYBRID: This type of PMP is a group of disease which lies between the above two explained grade types.
How does PMP spread?
- PMP does not spread through the bloodstream or lymphatic system and it is a unique type of cancer.
- First, it spreads inside the stomach (abdomen). Symptoms become visible when the mucus accumulates inside the abdomen.
- Before the symptoms show up, this condition is usually slow growing and it takes few years forthis type of cancer to develop fully.
Affected population
- PMP can affect both men and women in equal numbers. In the examination of appendiceal specimens, neoplasms have been found only in 1% of people. Among that, it’s been shown that an intestinal neoplasm has accounted only for one half of one percent of the people.
- 50% of these intestinal neoplasms are identified as carcinoid tumors and not PMP.
The occurrence of PMP is one per one million per year and it can be found in two out of every 10,000 cases of people who have gelatinous ascites. It is very difficult to diagnose this condition. The median age of people affectedby this disease is nearly 54, and in most of the cases, the disease is identified accidentally during the course of treatment carried out for some other medical problems.
Sources
- http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/pseudomyxoma-peritonei
- www.rarecancers.org.au/…/pseudomyxoma-peritonei-appendix-cancer
- www.macmillan.org.uk/…/pseudomyxoma-peritonei-pmp
- globalgenes.org/…/
- http://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/appendix-cancer/introduction
- http://www.cancercenter.com/appendix-cancer/types/
- https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/pseudomyxoma-peritonei/
- https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/7488/pseudomyxoma-peritonei
- www.pseudomyxomasurvivor.org/…/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7503361
Further Reading
- All Pseudomyxoma Peritonei Content
- Pseudomyxoma Peritonei Diagnosis
- Pseudomyxoma Peritonei (PMP) Research
- Treatment Options for Pseudomyxoma Peritonei
- Symptoms and causes of pseudomyxoma peritonei (PMP)
Last Updated: Feb 27, 2019
Source: Read Full Article