HPV vaccines that work in US women may miss the target in women from other countries

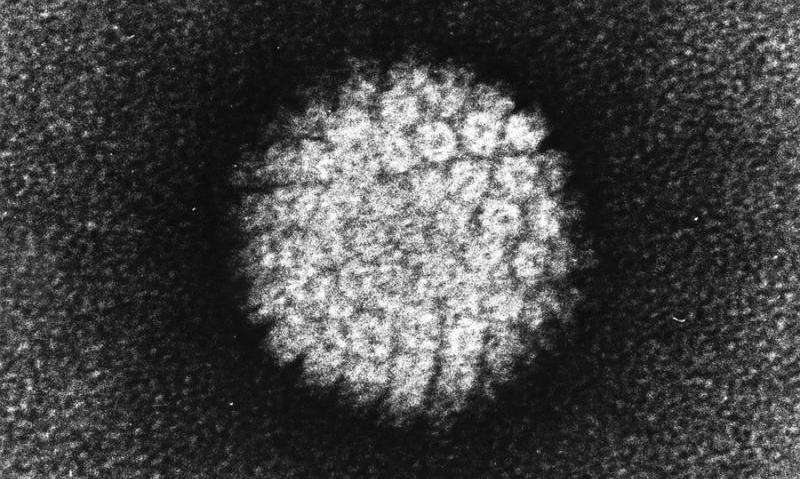
A research team at Dartmouth’s and Dartmouth-Hitchcock’s Norris Cotton Cancer Center has found that the same vaccination programs that target human papillomavirus (hrHPV) strains in the United States may not be as effective in protecting other populations of women from the disease. Years of work in Honduras, led by Gregory J. Tsongalis, Ph.D., has shown a very different prevalence of hrHPV there compared to the U.S. The majority of cervical cancers are caused by persistent infection with hrHPV with different vaccines available to protect against HPV infection. These findings, “HPV, Vaccines, and Cervical Cancer in a Low- and Middle-Income Country” are newly published in Current Problems in Cancer.
“After testing 2,645 women from multiple locations in Honduras for types of hrHPV and finding the prevalence of virus types to be quite different from those in the U.S., we asked what vaccine would be the most efficacious for the local situation, and which hrHPV types are most commonly found in cervical cancer tissues from Honduran women,” says Tsongalis. “The divalent vaccine against two HPV types and quadrivalent vaccine against four HPV types would only protect approximately half of women infected with this virus in Honduras. The most expensive vaccine would protect the majority of women, however many vaccination programs in low- and middle-income countries use the less costly vaccine, and these vaccines are not providing adequate protection.”
Source: Read Full Article