Gender-specific differences in the progression of rheumatoid arthritis discovered

Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic joint inflammation that leads to functional impairment in many sufferers. There are gender-specific differences in the emergence and development of this disease.
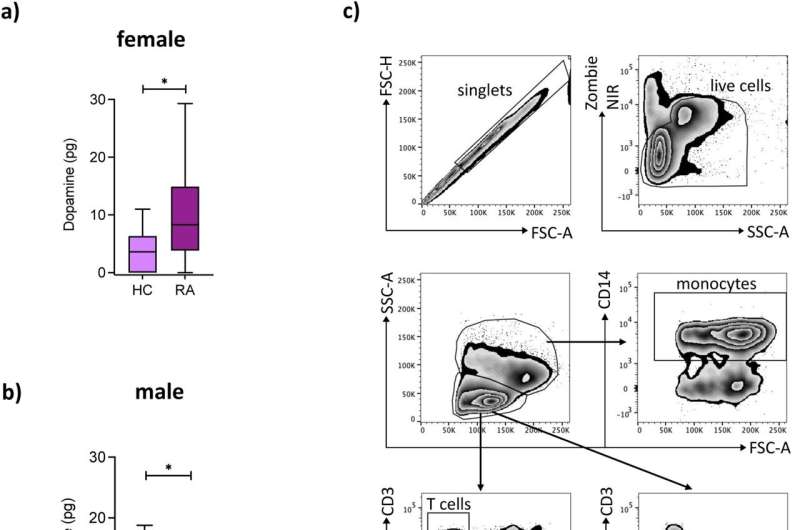
Researchers at the Leibniz Research Center for Working Environment and Human Factors in Dortmund (IfADo) have therefore examined the role of the neurotransmitter dopamine in rheumatoid arthritis with particular reference to gender differences. The results point to gender-specific differences in the dopamine-regulated signaling pathway in B cells, whereby dopamine may even have a pro-inflammatory effect in women.
Prof. Dr. Silvia Capellino’s group has identified involvement of the dopamine-regulated signaling pathway in B cells. This influence on immune cells of RA patients is gender-specific. The observed bifurcation of the dopamine-regulated signaling pathway between male and female RA patients can be used for therapeutic approaches in women in the future.
The influence of dopamine on certain cells of the immune system and thus on the course and development of rheumatoid arthritis discovered in the studies correlated with the duration of the disease and the functional disability in the female RA patients. Based on these findings now published in Scientific Reports, a diagnostic marker can be used in women.
Dopamine influences immunity
Women get rheumatoid arthritis more often than men. Not only the frequency, but also the progression of the disease differs between men and women. One possible explanation for this is the different role of sex hormones in immune reactions. Estrogens can directly influence the immune system and usually lead to inflammation.
Source: Read Full Article