Case report and review of a novel chromosomal abnormality in AML patient
Reviewers’ Notes
A new research paper was published in Genes & Cancer on June 28, 2023, entitled, "A novel t (5; 17) (q35; q21) associated with t (8; 21) (q22; q22) in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia: case report and review of literature."
The t (8; 21) (q22; q22) with the resulting RUNX1- RUNX1T1 rearrangement is one of the most common cytogenetic abnormalities in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). It is associated with a favorable prognosis. The t (5; 17) (q35; q21) is an uncommon translocation, fuses the gene for the nucleophosmin (NPM) to the retinoic acid receptor α(RARA) and was described essentially in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) variant.
In a new paper, researchers Kmira Zahra, Wided Cherif, Gereisha Ahmed, Haifa Regaieg, Ben Sayed Nesrine, Monia Zaier, Wided Mootamri, Yosra Ben Youssef, Nejia Brahem, Halima Sennana, and Abderrahim Khelif from Farhat Hached University Hospital-Sousse-Tunisia present the case of a 19-year-old male patient who developed an AML with t (8; 21) (q22; q22) associated to t (5; 17) (q35; 21).
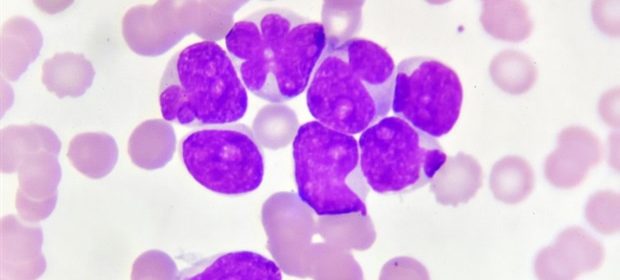
Morphology and immunophenotype of the leukemic cells were compatible with AML. The patient received chemotherapy based on cytarabine and anthracycline without all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) followed by allogenic stem cell transplantation in first remission. To the best of the researchers' knowledge, this is the first report of an association between a rare translocation t (5; 17) and t (8; 21) in AML.
"In this report, we will discuss the prognosis of this association as well as the treatment."
Impact Journals LLC
DOI: 10.18632/genesandcancer.232
Posted in: Medical Science News | Medical Condition News
Tags: Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia, Anthracycline, Bone, Bone Marrow, Cancer, Cell, Chemotherapy, Gene, Genes, Genomics, Hospital, Leukemia, Morphology, Myeloid Leukemia, Receptor, Research, Retinoic Acid, Stem Cells, Tumor