Hyperpigmentation and Acne

Although skin problems are often associated with those in adolescence, there are several conditions which can affect anyone at any age. Acne is one of the most common skin conditions in the United States and is thought to affect four out of five teenagers. Hyperpigmentation is also one of the most common reasons for visiting a dermatologist.
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Pigmentation changes such as melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation are common reasons to visit a dermatologist. Pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin. Changes in skin pigmentation tend to be more common among darker-skinned persons, including those of Asian, African, or Caribbean descent. Hyperpigmentation on the face, in particular, can often be seen in pregnant women or those using oral contraceptive pills. Acne can also cause hyperpigmentation. Hyperpigmentation can result from the overproduction of melanin or due to irregular dispersion of pigment in the skin secondary to cutaneous inflammation.
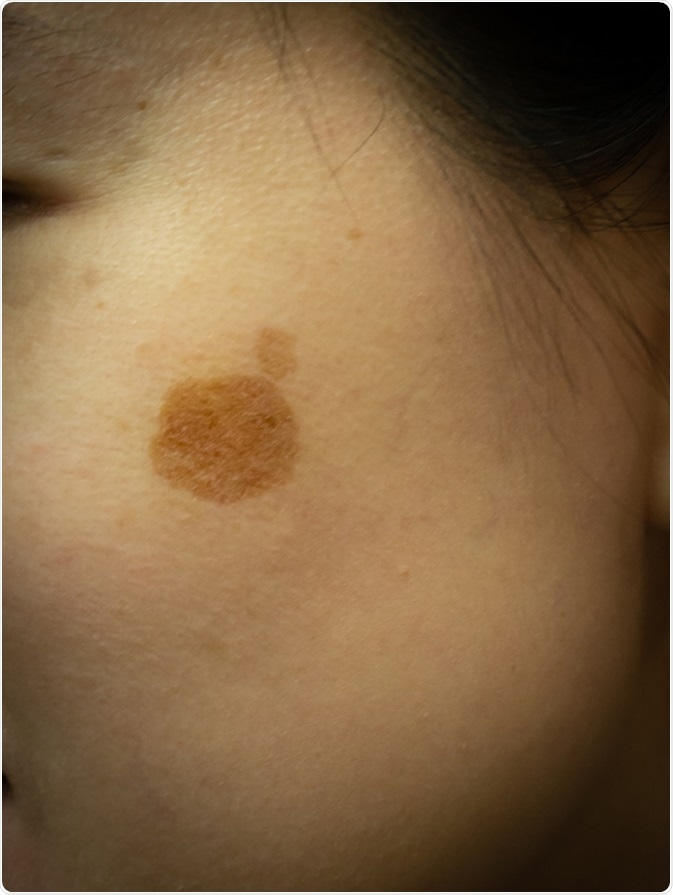
What is the Treatment for Hyperpigmentation?
It is important to note that, in some cases, hyperpigmentation may improve without the need for treatment. However, there are several self-management and treatment options for more severe cases. Treatment of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation should start promptly and should focus primarily on managing the underlying inflammation.
Limited Sun Exposure
For those with hyperpigmentation, the use of high-factor sunscreen and avoidance of excessive sun overexposure are recommended.
Light Therapy
Laser and light therapy have been found to be effective in treating cases of hyperpigmentation. Specifically, blue light photodynamic therapy and fractional photothermolysis.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels are a common cosmetic procedure that involve the application of chemicals of varying strength to destroy portions of the epidermis and dermis. Superficial peels penetrate the papillary dermis and are used to treat mild skin conditions such as hyperpigmentation. Caution is advised, as persons with darker skin may actually experience worsened pigmentation after using chemical peels.
Prescribed Treatments
Primary treatment for hyperpigmentation start with a course of topical depigmenting ointment. Specifically, retinoids and tretinoin may be beneficial in reducing hyperpigmentation in those with sun-damaged skin. Additionally, topical steroids may provide relief if there is an underlying inflammatory process. However, steroid creams can also cause thinning of skin tissue. Therefore, it should be used cautiously.
What is Acne?
Most people will experience bouts of acne during their lifetime. It can affect the face, back and chest and causes those areas to be populated with spots, as well as producing oily skin and skin that is generally sore or hot to touch. There are several types of spots that acne can cause, and complaints of acne can range from mild to moderate and severe. The severity depends on the types of spots experienced.
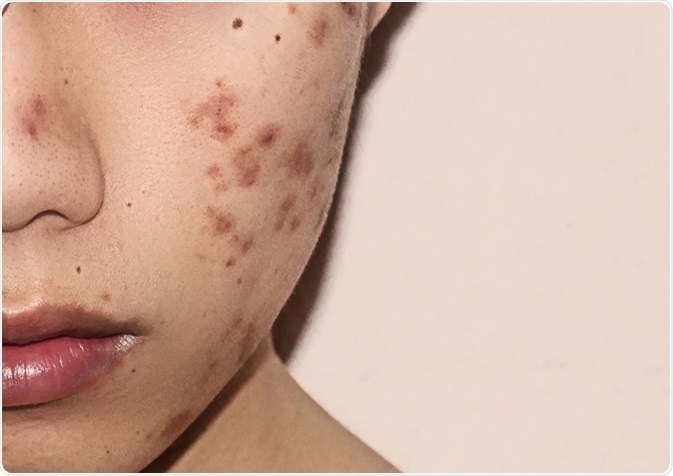
What Causes Acne?
Most cases of acne are linked to hormonal changes during puberty. However, adults are also known to develop the condition. Increases in hormone levels can trigger oil-producing glands situated next to hair follicles to produce increased amounts of sebum. The combination of excessive oil production and dead skin cells can plug hair follicles. This can result in the formation of spots, some of which are discussed below.
Cysts
These acute lesions resemble large lumps that are often pus-filled. Those who develop cysts are at the most risk of developing permanent scarring.
Nodules
Nodules are large hard lumps that are uncommonly seen on the skin surface and can be painful.
Papules
Papules are small red bumps that often feel sore or tender to touch.
Blackheads
Blackheads are small bumps, black or yellow in color. Their dark color is due to the lining of the hair follicles which produce pigment.
Whiteheads
Whiteheads tend to be firmer to touch and don’t ooze when squeezed.
Pustules
Pustules are similar to papules but have a white tip in the center from pus build-up.
What are Treatments for Acne?
Mild cases of acne can often be treated by over-the-counter medicine. However, for moderate to severe cases, additional medical attention might be required. Several drugs and ointments can be prescribed to treat acne, including topical retinoids, azelaic acid, topical antibiotics, antibiotic tablets, and isotretinoin. In some cases, oral contraceptive pills are prescribed to women to stabilize hormonal levels. A combination of antibiotic tablets and topical treatments are often prescribed for severe cases.
Sources
- Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation: A Review of the Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Treatment Options in Skin of Color: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2921758/
- Acne: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/acne/
- Are Natural Ingredients Effective in the Management of Hyperpigmentation? A Systematic Review: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5843359/
- The impact of acne and facial post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation on quality of life and self-esteem on newly admitted Nigerian undergraduates: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5955012/
- Chemical peels in the treatment of acne: patient selection and perspectives: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6053170/
Further Reading
- All Acne Content
- Acne
- Acne Causes
- Acne Treatments
- Acne and Women
Last Updated: Nov 26, 2018
Source: Read Full Article