Pharmacy researchers receive patent for chemical probe


Many brain diseases and disorders lead to neuroinflammation, a swelling of brain tissue that is increasingly recognized as one ofthe telltale signs and disease progression factors of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Neuroinflammation can limit blood flow to areas in the brain, which can lead to the inhibition of the body’s natural disease fighting mechanisms.
Traumatic brain injuries also cause significant neuroinflammation. In fact, unresolved and severe brain edema (swelling caused by trapped fluid) is the leading cause of death for traumatic brain injury patients within the first few days of injury.
Because neuroinflammation has been linked to dopaminergic signaling, Nadia German, Ph.D., director of the Medicinal Chemistry program at the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) Jerry H. Hodge School of Pharmacy, said there is increasing interest in determining whether the modulation of dopamine levels at the inflammation site can stop or even reverse neurodegeneration.
To help make that determination, German and collaborator Constantinos Mikelis, Ph.D., adjunct associate professor in the TTUHSC Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, have received a U.S. patent for a chemical that targets the brain’s dopamine transporter. Affecting the dopamine transporter is one of the ways by which dopamine levels in the brain can be controlled.
In addition to Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and traumatic brain injuries, German said there are other central nervous system disorders, such as glioblastomas (brain tumors) and multiple sclerosis, that also exhibit dopamine-related neuroinflammation, and that could potentially benefit from the newly patented chemical probe.
“Low levels of dopamine can result in neuroinflammation, neuron death and other non-pleasant effects,” German said. “At the same time, neuroinflammation causes reduction in the expression of dopamine neurons, creating a vicious cycle of cause and effect. By controlling the dopamine levels, we can try to stop this cycle.
“The specific component we have patented has really great selectivity for the dopamine transporter. It does have some activity at another transporter that regulates the neurotransmitter serotonin, but its affinity to the dopamine transporter is higher—by one hundred-fold—so it’s really, really selective.”
The Mikelis lab evaluated the different activities displayed by the patented molecule in relation to the various receptors. He also investigated the pharmacokinetic profile of the molecule to ensure it actually reaches the brain at levels that are beneficial to the patient.
“We used in vitro (outside a living organism; e.g., test tube, culture dish) and in vivo (in a living organism) models, and we tested different molecules to identify the best possible parameters and to select the molecule that we finally patented,” Mikelis added.
German and Mikelis patented the molecule as a chemical scaffold, a process that adds desired bioactive properties to the core structure of the molecule.
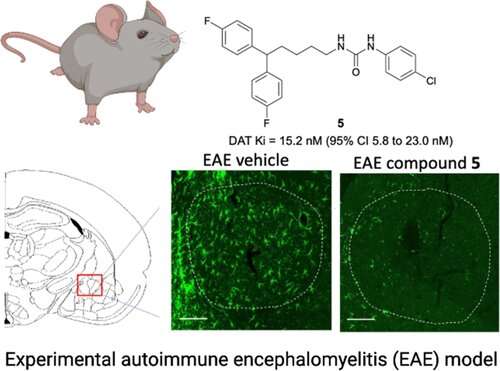
“Together with our very supportive collaborators Dr. Volker Neugebauer and Dr. Mirla Avila, we just recently published a paper in the journal ACS Chemical Neuroscience where we talk about this,” German said. “To our best knowledge, we are the first to show that dopamine transporter inhibitors reduce levels of neuroinflammation in multiple sclerosis models (mice) at the same level or better than the corticosteroids that we use now.”
Though the testing and evaluation that led to the patent demonstrated that the specific activity of the molecule has a strong therapeutic potential, it still must pass through several stages of development and approvals before it can become a market-ready drug.
“It will take some time, I’m sure, but in the end, I’m also sure we will be able to get a molecule with a good drug-likeness profile,” German said. “The gold standard, of course, is oral dosing, but if not, there are many systems we can use for the delivery of the drug.”
Source: Read Full Article